Plasma residues enhance bacterial attachment to platelet storage bags
In brief...
Bacterial attachment inside platelet concentrate bags is enhanced by plasma residues
and is not altered by the type of storage bags used.
At Canadian Blood Services, PCs are produced by two different methods: apheresis and pooled platelets. Apheresis is a donation of platelets from one donor, suspended in the donor’s plasma for storage. Pooled platelets are prepared by combining platelets from four different donors with the plasma from one of the four donations to make one unit of pooled platelets. The storage bags for these two platelet products have distinct texture patterns on the inner surfaces of the bags. A greater understanding of S. epidermidis biofilm formation would help Canadian Blood Services develop strategies to continue ensuring the highest quality and safety of the products that we produce for patients
What did the researchers do?
To identify which factors influence the adherence of S. epidermidis to the inner surface of the PC collection bags, the researchers examined bacteria biofilm growth in both kinds of PC storage bags (apheresis bags and pooled platelets bags), with and without residual platelets or plasma. To coat bags with PCs, the researchers drained the product from one freshly collected apheresis PC unit and one pooled platelets PC unit. The plasma-coated bags were obtained by filling a sterile apheresis bag and a sterile pooled platelets bag with plasma and incubating with agitation for 24 hours at room temperature for preconditioning. The plasma was then drained, allowing plasma residues to remain.
The bags were filled with culture media which promotes the growth of bacteria. Low levels of bacteria were added to each bag and incubated with agitation for seven days at room temperature to allow for bacterial growth. On day seven, the culture media was removed and the bacteria attached to the bags were dislodged using high-energy sound waves. Bacteria levels were determined by growing the bacteria on plates and counting the colonies. The researchers also used high-powered microscopes (scanning electron microscopy) to confirm bacterial attachment to the bags.
To test whether a plasma protein called fibrinogen, which interacts with many kinds of pathogenic bacteria, influences the ability of S. epidermidis to attach to PC bags, fibrinogen was removed from plasma using a snake venom enzyme named ancrod. The PC bags (apheresis bag and pooled platelets bag) were coated with fibrinogen-free plasma to test bacterial attachment, following the same protocol as described above.
What did the researchers find?
- Bacterial attachment and formation of undesirable biofilms is significantly higher in bags coated with PC or plasma residual materials compared with uncoated bags.
- However, S. epidermidis adheres equally to both bag types (apheresis bag and pooled platelets bag) in the presence of PC or plasma residual material.
- Fibrinogen removal did not alter adherence of bacteria to PC and plasma-coated bags.
How can you use this research?
The results of this study indicate that the ability of S. epidermidis to adhere to both types of PC storage bags is increased by plasma residues coating the inner walls of the bags. It is known that plasma proteins can attach to the plastic material. Thus, it is possible that the plasma residues attached to the PC bags might serve as a scaffold for bacterial adhesion, leading to biofilm formation. The researchers showed that the different textures of the two PC storage bag types do not impact biofilm formation. This is important information for Canadian Blood Services as we continue to improve the safety of PCs that Canadian patients receive.
This study attempted to understand the role of fibrinogen on bacterial attachment to PC bags; unfortunately, complete fibrinogen removal from plasma was not possible and residual fibrinogen supported bacterial adhesion to the platelet bags. It is hypothesized that other plasma proteins contributed to bacterial attachment in the experimental settings used in this study. These results merit further investigation using human serum, which is fibrinogen-free, to test bacterial attachment in the absence of plasma proteins.
Although the researchers used realistic initial bacterial loads in the experiments of this study, a limitation of the experimental design was that bacterial attachment was only measured after seven days of incubation when bacterial levels were high and biofilms were formed. Since no differences in bacterial adhesion were seen between the two kinds of PC bags, monitoring of bacterial adhesion at different growth stages could be performed as a follow up study with simpler testing using one bag type.
Importantly, adhesion of bacteria to PC bags has a negative impact on PC safety, even with very low bacteria levels, as it decreases detection during routine screening. Thus, finding strategies to reduce plasma residues attaching to the inside of PC storage bags is a recommended area of focus. Innovative technologies aimed at decreasing bacterial attachment to PC bags — therefore tackling the existing bacterial contamination risk in PCs — are also encouraged to enhance the safety of PC transfusion for patients.
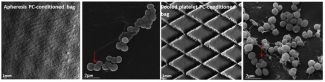
Caption: Bacterial attachment was confirmed in both bag types coated with PCs. Red arrows point at a single S. epidermidis bacterium
About the research team
The senior author, Dr. Sandra Ramirez-Arcos, is a development scientist with the Product and Process Development group at the Canadian Blood Services Centre for Innovation and an adjunct professor at the University of Ottawa. Dr. Maria Loza-Correa is a postdoctoral fellow in the research group of Dr. Ramirez. Dr. Qi-Long Yi is a senior biostatistician at Canadian Blood Services. Dr. Miloslav Kalab is a retired research scientist at Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada. Dr. William Sheffield is associate director research and senior scientist at Canadian Blood Services Centre for Innovation, and professor at McMaster University.
This research unit is derived from the following publication(s)
[1] Loza-Correa M, Kalab M, Yi Q-L, Eltringham-Smith LJ, Sheffield WP and Ramirez-Arcos S: Comparison of bacterial attachment to platelet bags with and without preconditioning with plasma. Vox Sanguinis 2017. [Epub ahead of print]
Acknowledgements: This research received funding support from Canadian Blood Services (Product and Process Development Program and Postdoctoral Fellowship awarded to Dr. Loza-Correa), funded by the federal government (Health Canada) and the provincial and territorial ministries of health. The views herein do not necessarily reflect the views of the federal, provincial, or territorial governments of Canada. Canadian Blood Services is grateful to the blood donors who made this research possible. This Research Unit was prepared by Dr. Maria Loza-Correa in collaboration with the knowledge mobilization group.
Keywords: platelet concentrates, plasma, bacterial contamination, platelet bags
Want to know more? Contact Dr. Ramirez-Arcos at sandra.ramirez@blood.ca
Plasma residues enhance bacterial attachment to platelet storage bags (PDF)